Outline of Suicide Countermeasures
What are Suicide Countermeasures
Suicide countermeasures shall be vigorously and comprehensively promoted at the three levels of “personal support,” “regional cooperation” and “the social system” in ways that will lower the risk of suicide in society as a whole by reducing the social factors that are impediments to life (suicide risk factors) and increasing those that enhance it (protective factors against suicide). A comprehensive approach is important, one that focuses not only on mental health but also has a social and economic component. And, in order to implement this comprehensive approach, close coordination is needed among policy measures, people and organizations in a variety of fields.
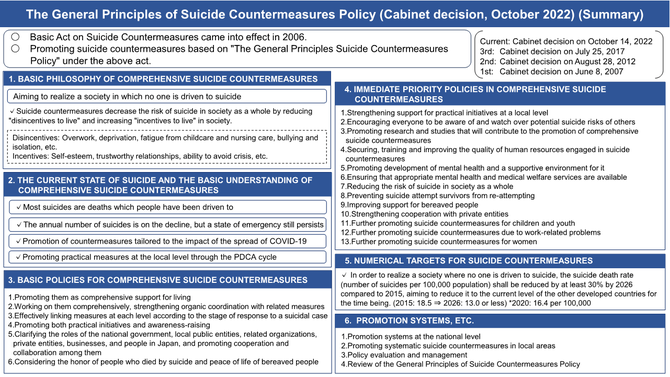
Based on the Basic Act on Suicide Countermeasures (Enacted in 2006, revised in 2016), the government has formulated the General Principles of Suicide Prevention Policy(Cabinet decision in 2007, revised in 2022) as a guideline, under which suicide countermeasures in Japan is promoted.
- The General Principles of Suicide Countermeasures Policy, Summary(Japanese)*
- The General Principles of Suicide Countermeasures Policy, Summary(English - Provisional Translation)
- The General Principles of Suicide Countermeasures Policy(Japanese - Original)*
- The General Principles of Suicide Countermeasures Policy (English - Provisional Translation)*
(*cf. Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, https://www.mhlw.go.jp/stf/taikou_r041014.html)
Suicide Countermeasures acts as inclusive support to stay alive
Lowering the risk of suicide in society as a whole by inclusive support including mental health, social and economic perspectives.
As the World Health Organization (WHO) clearly states that most suicides are social issues that can be prevented, we have shared a common understanding around the world that suicides are deaths that can be prevented by the efforts of society.
Suicide is related to a variety of factors in complex ways such as changes in the workplace and the community as well as health concerns, economic and livelihood issues and problems with personal relations, not to mention an individual’s personality traits, family circumstances and views on life and death.
As for social factors, such as unemployment, bankruptcy, multiple debts and long working hours, they can be solved by social initiatives such as reviewing existing systems/practices or enhancing counseling/support systems. Moreover, even though some factors like health or family issues may at first glance seem to be the problems of a particular individual, here too there are many situations in which these problems can be resolved by extending a helping hand of social support in the form of professional counseling, treatment for depression, etc.
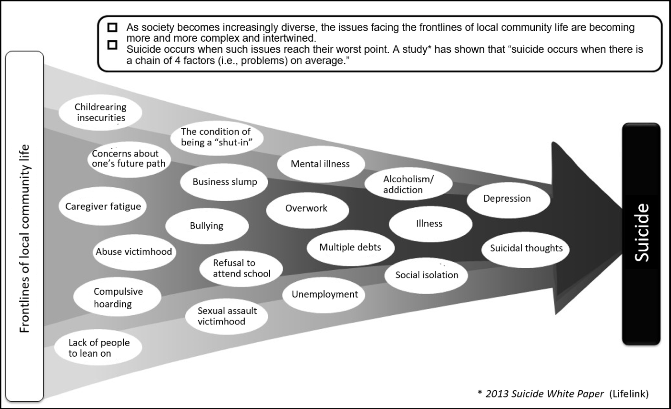
In light of the basic recognition that suicide is a death to which many have been driven and a social problem that can largely be prevented, suicide countermeasures shall be deployed as comprehensive support to stay alive from the stance of lowering the suicide risk in society as a whole and protecting the lives of each and every individual.
Decreasing life-impeding factors and increasing life-enhancing ones
It is said that, for both individuals and society, the suicide risk goes up when the factors that impede life (suicide risk factors) exceed those that enhance it (protective factors against suicide). To put it the other way around, suicide risk does not rise in the same way for a society or an individual even if they may be experiencing the same life-impeding problems such as unemployment, multiple debts, poverty.
The risk of suicide increases when the life-impeding factors exceed the life-enhancing factors such as self-esteem, reliable human relationships, and the ability to avoid a crisis. When these positive factors exceed the negative ones, the suicide risk does not go up.
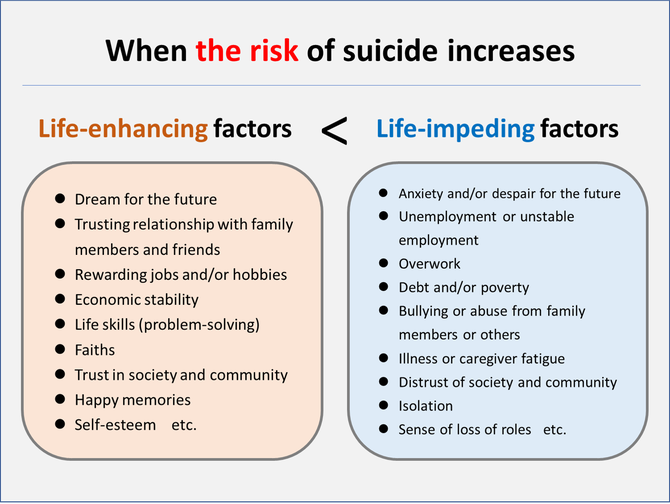
Therefore, suicide countermeasures need to be promoted as a comprehensive support to stay alive by lowering the suicide risk through both approaches, i.e., by making an effort to increase the life-enhancing factors as well as decrease the life-impeding ones.
Interconnecting policies and measures at each level: personal support, regional coordination and the social system
Individual policies and measures related to suicide countermeasures shall be comprehensively promoted, taking into consideration the following three levels and organically interconnecting them:
- Personal support level: Policies and measures to provide counseling and support that works to find solutions for the problems of each individual
- Regional coordination level: Policies and measures for practical coordination, etc., among the related organizations to provide comprehensive support to persons with complex problems
- Social system level: Policies and measures related to enhancing and revising the framework of laws, the General Principles, plans, etc.
This approach is the TIS model (Three-Level Model of Interconnecting Suicide Countermeasures) which is based on the idea of promoting three levels of measures in an integrated and linked manner; that is, strengthen interpersonal support in various fields, promote regional cooperation necessary to strengthen interpersonal support, and develop social systems necessary to promote regional cooperation, considering people’s livelihood as the most fundamental point.
In order to prevent suicide by enabling the person who is being driven to it to live safely and securely (i.e., to implement a comprehensive approach), close coordination is necessary among policy measures, people and organizations in a variety of fields.
Related New Topics
- November 28, 2025
- Call for papers : Suicide Policy Research (Volume 5, No. 1)
- October 9, 2025
- JSCP’s E-learning Training Program to Promote Suicide Countermeasures at Universities
- September 18, 2025
- Suicide Policy Research